At Willow, we do a lot of SEO audits, where we review sites for search engine best practices and help our clients increase organic traffic to their site. In the process, we often see the same technical oversights or issues over and over again. Whether we’re working with a big site or small, a retail site or a nonprofit association. Making sure your web developers understand the basics of technical SEO can help you avoid these kinds of faux pas from the start.
Here are just a few of the common recommendations we make:
1. Set up Google Search Console
Connecting Google Analytics is a pretty standard step in launching a new site, but people often forget to set up Google’s Search Console, as well. This tool is the best way to communicate with Google about your site, and it’s where you can submit sitemaps, look at search data, and see any crawl errors Google finds. You’ll also get more comprehensive search and keyword data from Search Console than you get from Analytics. It’s the first step towards getting actionable search data about your site.
Bonus Tip: Make sure you set up each version of your domain in Google Search Console (www, non-www, https) and set a preferred URL in the site settings.
2. Make sure Google can crawl your site
If Google can’t see the content on your site, it can’t index it. Be especially careful when using noindex directives, iframes, Javascript/AJAX, or even when putting important text in graphics—these techniques can all keep the Googlebot from seeing your content.
Bonus Tip: While there are ways to make Javascript or Ajax crawlable, Google only states that it is “generally able” to understand it correctly. It’s best to make sure all your pages fall back to a useable and readable page without Javascript.
3. Use alt text and descriptive file names
On a similar note, when you upload photos, graphics, videos, or other files, be sure to include alternate text and file names that identify the content of the file. For example, “ACME_logo.jpg” is much more useful than “img89345.jpg.” This can send ranking signals to search engines, boosting your chances of showing up in Google Image Search, and also helps search bots understand the context of a page.
Bonus Tip: Using image alt text not only helps search engines understand the content of an image (and any text that might be in the image), but it also improves accessibility for visitors using screen readers.
4. Choose a canonical URL
Duplicate content is a big search engine “no-no”—and while there are many ways duplicate content can be created across your site. One of the simplest and most basic is through failing to choose a canonical URL for your domain. Let’s say you can access your homepage through these three different URLs:
- http://www.example.com
- http://example.com
- https://www.example.com
These are technically three separate entities, all with the same content. Not only does that give Google duplicate content to crawl, but it also means that any SEO value you get from links pointing towards the different domains is split amongst them.
Google best practices tell us to choose one main version of the URL as your canonical and to redirect all other versions to this preferred URL.
Bonus Tip: We recommend using server-side 301 (permanent) redirects unless your redirect is truly temporary.
5. Pay attention to site speed
Google prefers to feature sites that provide a great user experience for searchers. This includes a quick load time whether on desktop or mobile devices. According to Kissmetrics, 47% of consumers expect a web page to load in 2 seconds or less—and a one second delay in page response can result in a 7% reduction in conversions! That makes it worth the time to make sure you optimize images, compress resources, and use other strategies to improve page load time.
Bonus Tip: Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool to see how your pages stack up—and check out the “Site Speed” section of Analytics under “Behavior” for average page load time across your domain.
6. Use semantic markup
From schema.org vocabulary to something as simple as ensuring headings are in <H> tags within the HTML, semantic markup helps search engines like Google better understand your content. Schema attributes, like those that identify reviews, price, or even calories in a recipe can also give Google clear information to add to your listing in search engines. This means more attention and more clicks—and it could even help your content show up in a Google Answer Box like this:
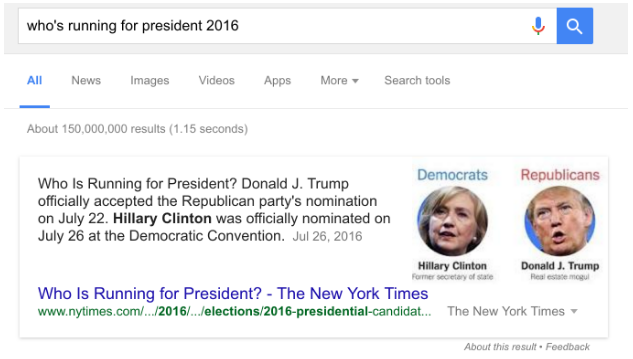
Bonus Tip: Use keywords in your heading tags to emphasize important topics for which you’d like to rank in search engines.
7. Design sites to be responsive
Last but not least, Google has rolled out several algorithm updates that give sites a better ranking for boosts to mobile-friendly websites. Having a responsive site that will adjust to the user’s device, whether they’re on a smartphone, tablet, or desktop computer, means you’re always putting your best foot forward and showing visitors a user-friendly site.
Bonus Tip: Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check specific URLs on your site—and check out the “Mobile Usability” section in Google Search Console for recommendations for your entire domain.
Hungry for more? Willow can perform an SEO audit of your website, so you can ensure you’re following best practices not only for technical issues like these, but also for content optimization and external ranking signals. Contact us today to make your site SEO-friendly.
